-
Singlet Fission in a Flexible Bichromophore with Structural and Dynamic Control
A. Aster, F. Zinna, C. Rumble, J. Lacour and E. Vauthey
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 143 (2021), p2361-2371


DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c12384 | unige:148899 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
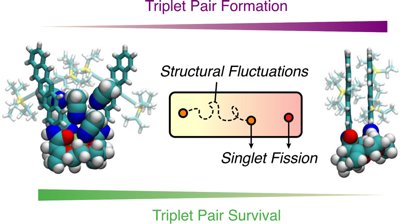
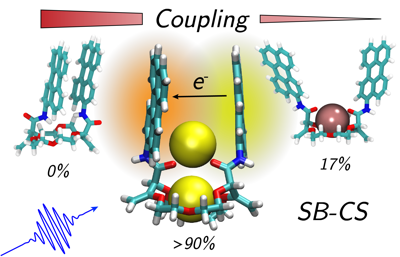
Singlet fission (SF), i.e., the splitting of a high-energy exciton into two lower-energy triplet excitons, has the potential to increase the efficiency for harvesting spectrally broad light. The path from the photopopulated singlet state to free triplets is complicated by competing processes that decrease the overall SF efficiency. A detailed understanding of the whole cascade and the nature of the photoexcited singlet state is still a major challenge. Here, we introduce a pentacene dimer with a flexible crown ether spacer enabling a control of the interchromophore coupling upon solvent-induced self-aggregation as well as cation binding. The systematic change of solvent polarity and viscosity and excitation wavelength, as well as the available conformational phase space, allows us to draw a coherent picture of the whole SF cascade from the femtosecond to microsecond time scales. High coupling leads to ultrafast SF (<2 ps), independent of the solvent polarity, and to highly coupled correlated triplet pairs. The absence of a polarity effect indicates that the solvent coordinate does not play a significant role and that SF is driven by intramolecular modes. Low coupling results in much slower SF (∼500 ps), which depends on viscosity, and leads to weakly coupled correlated triplet pairs. These two triplet pairs could be spectrally distinguished and their contribution to the overall SF efficiency, i.e., to the population of free triplets, could be determined. Our results reveal how the overall SF efficiency can be increased by conformational restrictions and control of the structural fluctuation dynamics.